
Share
The Future of Zero Trust in Modern Cybersecurity
In the modern world beholding diverse types of cyberthreats and attacks, data breaches, ransomware attacks, and hacks with each passing day, it is essential to be proactive rather than reactive! In Q1 2024, Check Point Research (CPR) witnessed a significant rise in the average number of cyber-attacks per organization per week, reaching 1308, which denotes a 5% increase from Q1 2023 and a 28% increase from the last quarter of 2023. These numbers are indeed a grim reminder to combat the ever-evolving cyberthreat landscape.
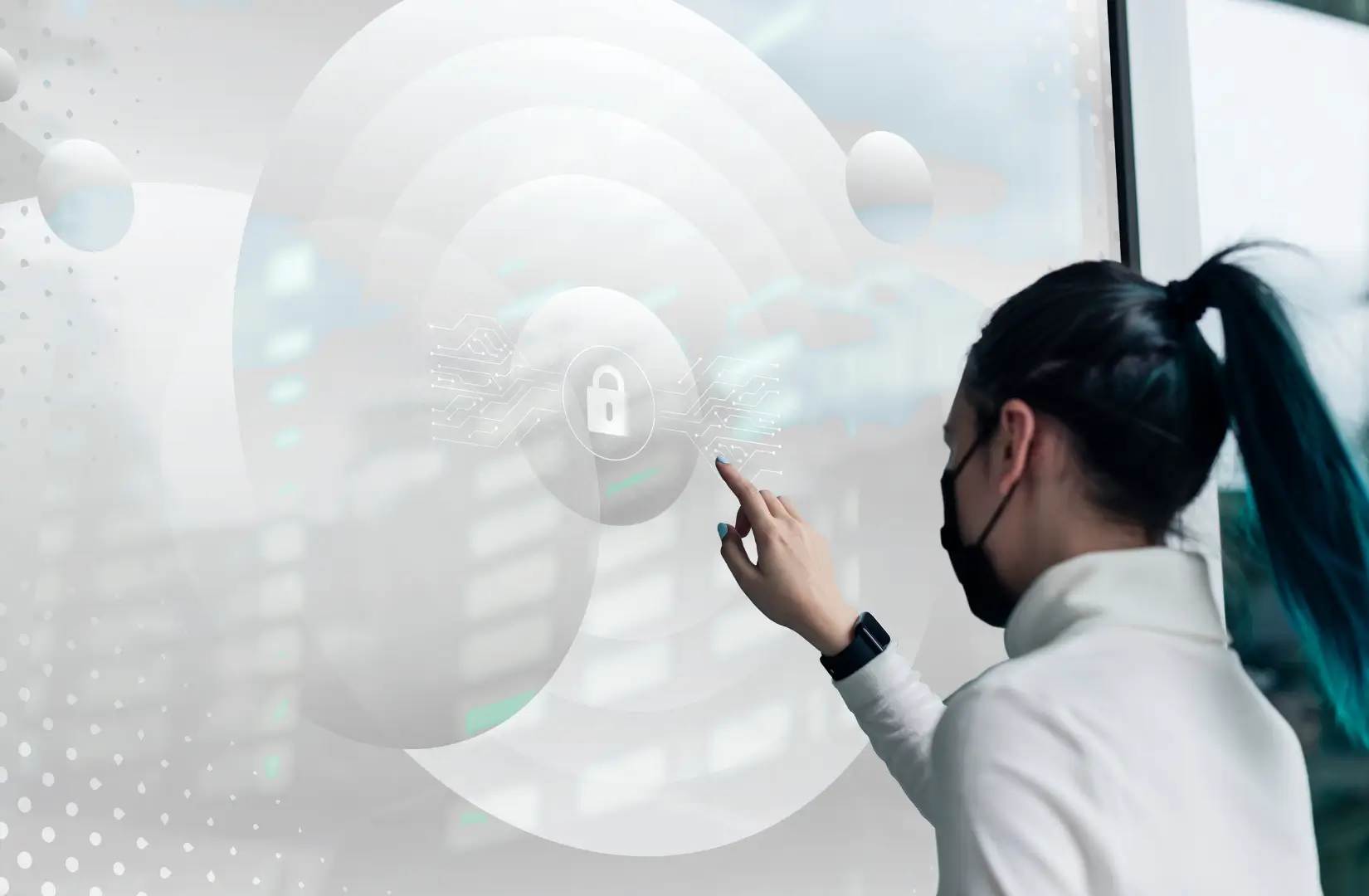
Amidst a swarm of cybersecurity trends surfacing the industry in 2024, Zero Trust has gained huge traction and is expected to witness a greater adoption in the coming years. Especially in the current, modern environment where hybrid physical and cloud environments are bagging widespread popularity, Zero Trust security model has evolved into a cornerstone of the modern cybersecurity realm, protecting devices, apps, people, and data irrespective of their network location.

What is Zero Trust in Cybersecurity
Zero Trust is an end-to-end security principle that restricts all accesses by default. Unless authenticated, authorized, and validated before granting access, no user, application, or device can be trusted, and no digital interaction can take place. This validation at every access point reduces the number of unauthorized users or systems accessing the networks and prevents security breaches.
Besides increased protection against cyberthreats, the benefits of Zero Trust security model include greater visibility into the network, stronger security posture, granular access control, flexible and adaptive security controls, simpler security implementations, adherence to regulatory compliances and standards, reduced remediation and recovery costs, and much more.
Core Design Principles
Beyond providing proactive and frictionless security, Zero Trust security model fosters businesses to operate more effectively and efficiently, outclassing as the future of cybersecurity. This model is based on three core design principles including “Never Trust, Always Verify”, “Assume Breach”, and “Principle of Least-Privileged (PoLP)”. Akin to its literal meaning, “Never Trust, Always Verify” means always authenticate and verify across all data points including location, device, service or user identity, considering everything and everyone as potential threats. Every access request is put through the concept – “I have zero trust in you and must verify you before trusting and granting access to the resource you require”.

“Assume Breach” is a pessimistic design principle that lets the organization assume that its network has already been infiltrated, thereby preventing the occurrence of any breach or its impact if occurred. Organizations devise defense solutions, segment access and decrease the attack surface, verify end-to-end encryption, and continuously monitor for vulnerabilities throughout the network.
The other design principle that Zero Trust security model depends on is “Principle of Least Privilege (PoLP)”, which denotes that users only have access to what they truly need to pursue their responsibilities and no more. It is believed that the more users have access to, the more negative impact is if their account is compromised, or a breach occurs. This principle thus prevents potential vulnerabilities, breaches, and cyberattacks from happening.
Key Trends of Zero Trust Security Model
API Security
The security of APIs stands at the forefront of most organizations today due to the presence of huge sensitive data and the severe consequences of breaches. It is here Zero Trust security model comes as a savior, wherein every API request is authenticated, authorized, and validated before any action is taken. Moreover, Zero Trust plays a major role in providing robust access controls, tackling overprivileged accounts, and ensuring restricted vendor access. With the integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) based solutions, the API security and management takes a leap further and creates advanced protection against cyberattacks.


Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM)
With businesses largely migrating to cloud environments and relying on cloud services, it is imperative that Zero Trust security implementation seamlessly integrates with cloud platforms, ensuring a consistent security posture across both on-premises and cloud environments. In particular, Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) will become a pivotal trend in Zero Trust security implementation. CSPM tools help identify misconfiguration issues, compliance risks, anomalous behavior, potential threats, and other cloud-based vulnerabilities, thus enabling businesses to continuously monitor and manage their cloud infrastructure. The CSPM operates based on an assumption that users will misconfigure services to create a greater risk exposure, thus avoiding the most common human errors and IT process vulnerabilities.
Identity and Access Management
The IAM market has evolved beyond the traditional concepts of Identity and Access Management towards a comprehensive identity threat detection and response framework. It is here Zero Trust security model brings the proactive identity threat prevention concept to the table, wherein potential network and host breaches across identity management systems are identified prior to their occurrence. Further, Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA), the pivotal aspect of Zero Trust, widely helps in verifying identities and prevents attackers from gaining access despite compromising a particular resource. MFA encompasses sophisticated methods such as biometrics, security questions, risk-based authentication, behavioral analytics, and others, ensuring only authorized individuals have access to resources and sensitive data.


Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA)
Unlike traditional VPNs which authenticate users only once and grant broad network access, Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) solutions grant secure access to only specific applications and resources based on user needs, minimizing the attack surface. ZTNA also prioritizes faster and streamlined access to applications and continuous user validation, marking the end of the VPN era. With enhanced usability, security, onboarding, and manageability, and many other advantages, ZTNA stands out as the alternative cybersecurity solution to VPN! Especially due to its scalability and adaptability to evolving business needs, rising cyber threats, cost-effectiveness, enhanced user experiences, adherence to compliances, and much more, ZTNA will witness a rise in adoption in 2024.
Regulatory Compliance
The integration with regulatory compliance has proven to enhance the functionalities of cybersecurity strategies like Zero Trust, especially in handling sensitive data across healthcare and finance industries. Zero Trust helps organizations address compliance requirements by protecting sensitive data and preventing data leaks, thus being closely related to the realm of cybersecurity. Further, Zero Trust facilitates compliance with regional standards such as General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA), Personal Information Protection and Electronic Documents Act (PIPEDA), Brazilian General Data Protection Act (LGPD), and others.


Integration of AI and ML
In today’s digital realm, the integration of AI and ML with Zero Trust security models stands paramount. This integration helps in analyzing user behavior and network patterns to identify anomalies and vulnerabilities, thus preventing the occurrence of security breaches beforehand. In fact, a significant portion of the investments in AI across the world is focused on enhancing cybersecurity, and is expected to exceed $300 billion by 2026, according to a report by IDC. This clearly denotes the imperative role of AI and ML in the advancement of Zero Trust security models.
Insights from a Cybersecurity Leader
When asked about the future of cybersecurity and the Zero Trust security model, Rajesh Paraman, Vice President - Security Engineering, Cloud Destinations, articulates, “Experts predict a gradual evolution, not a sudden revolution, for Zero Trust. It requires a fundamental shift in mindset, moving from implicit trust within the network perimeter to ‘never trust, always verify’ for every connection. Despite the emerging challenges including implementation complexity, striking the right balance between robust security and seamless user experience, and establishing a skilled cybersecurity workforce, the future of Zero Trust seems bright and is poised to evolve into a widely preferred cybersecurity philosophy. By addressing these challenges, organizations can build a more resilient security posture for the future and keep the Zero Trust momentum going!”

 Back
Back











 Linkedin
Linkedin








